Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development
RESEARCH LABORATORIES FAENZA
3D printing technologies
Additive manufacturing processes are applied to produce objects through the application of different layers of materials, allowing to create complex or functionalized structures, not obtainable by conventional methods. Additive manufacturing minimizes the mechanical machining, raw materials consumption and development time for new products. It is cost-effective for small-batch production and suitable for customized and on-demand products.
The Laboratory of Material Technologies Faenza develops printable suspensions/feedstocks, prints prototypes and small series, optimizes the thermal treatments, characterizes the raw materials and materials and qualify the printed components. The 3D printing of advanced ceramics, polymers and metals is developed for different applications: biomedical, transport, energy, aerospace, creative industry, cultural heritage, etc.
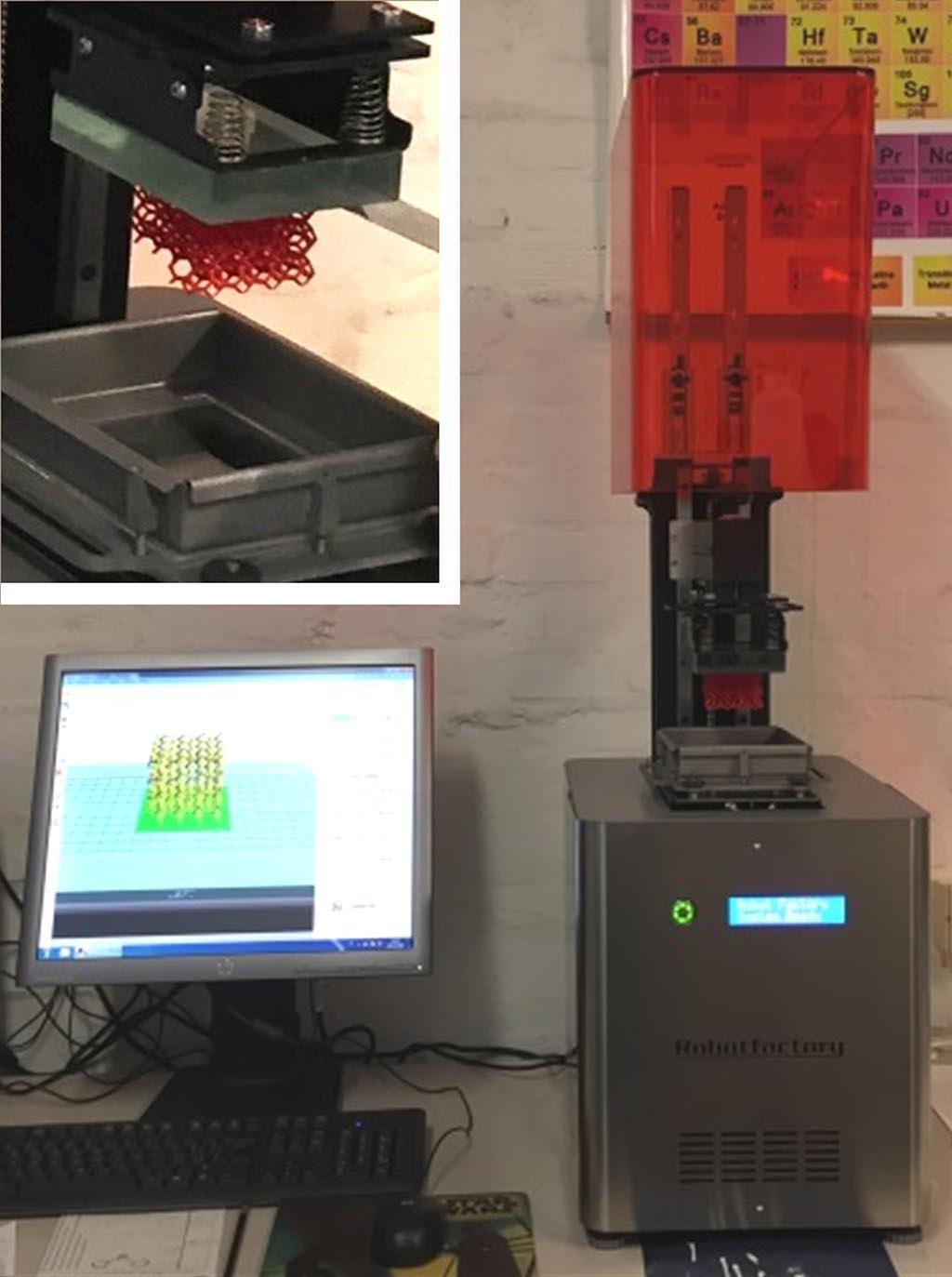
Digital Light Processing
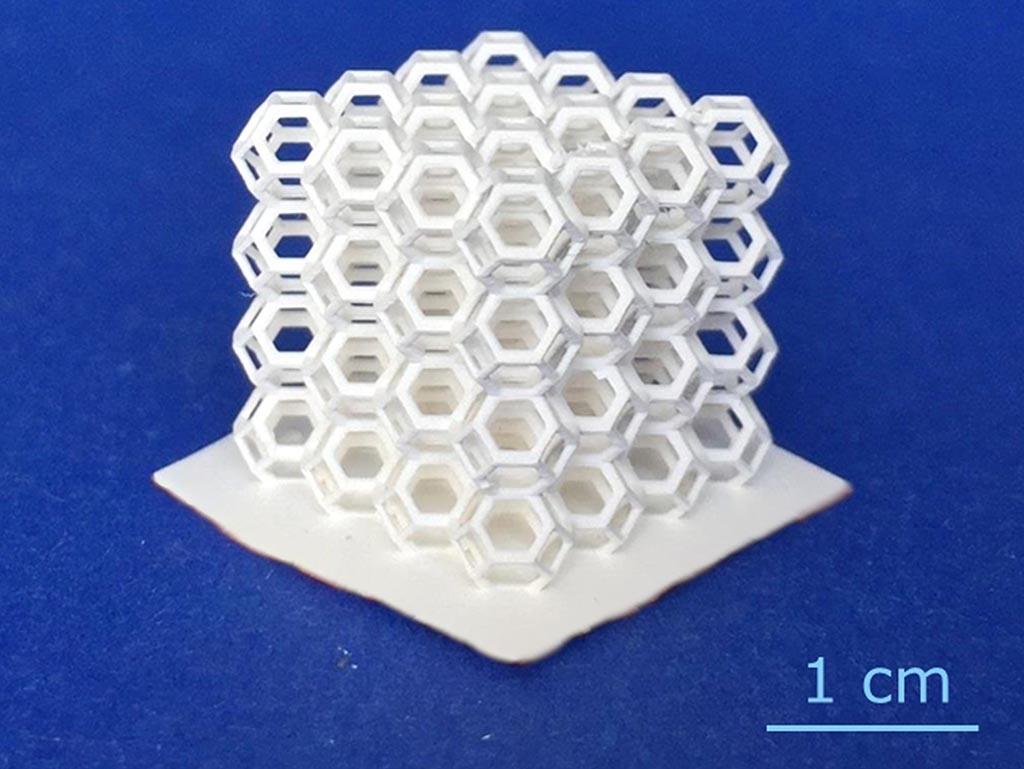
Development of photocurable slurries and 3D printing of prototypes and small series with the Robotfactory 3DLPrinter-HD 2.0+ (construction volume L 100 x W 56 x H 150 mm).
The slurry is selectively consolidated layer by layer through the polymerization by means of UV-visible beam light from a projector starting for a CAD file. Complex geometries with a high degree of detail and a good surface finishing are achieved.
The Digital Light Processing (DLP) technology can be applied for the 3D-printing of advanced ceramics, composite ceramics, resins or metals.
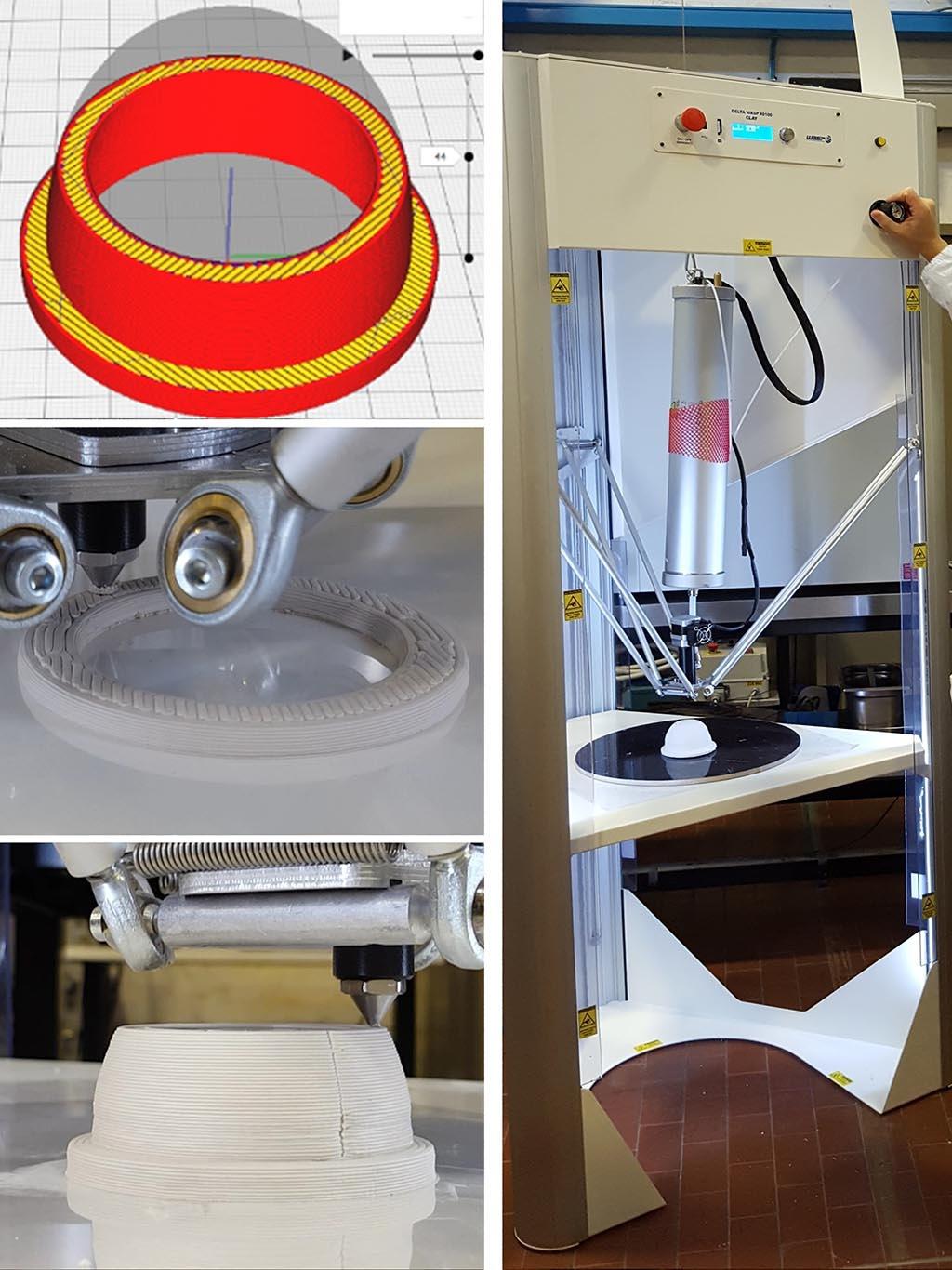
Liquid Deposition Modeling
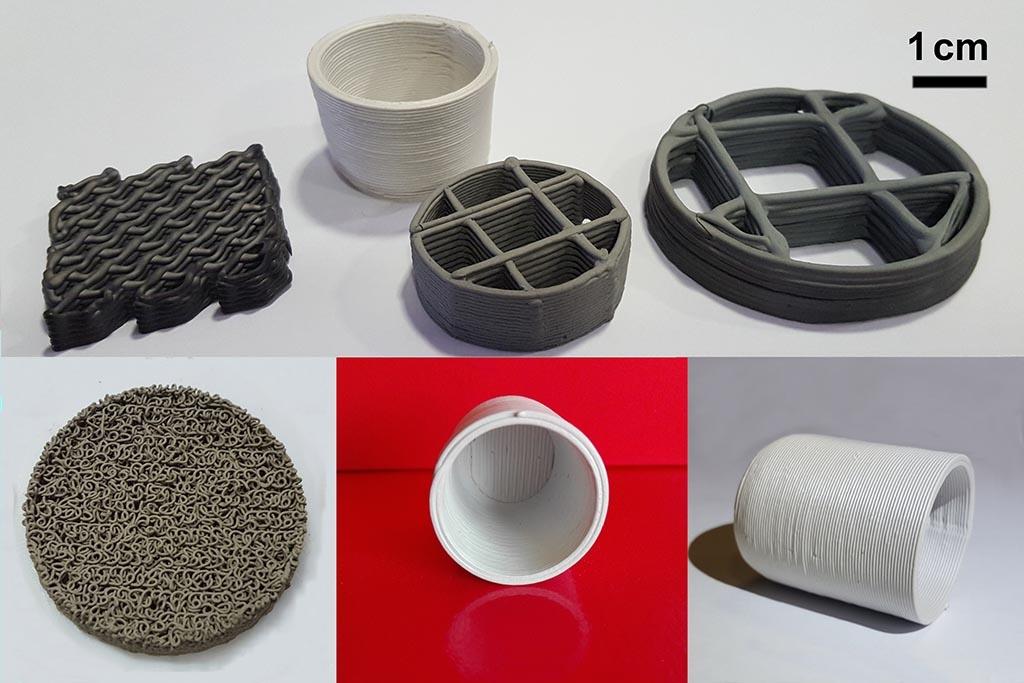
Development of extrudable ceramic pastes and 3D printing of prototypes and small series with the Delta 40100 Clay - WASP printer (construction volume f 100 x H 1500 mm). The ceramic paste is extruded as a filament while the nozzle is moved across the construction platform starting from a CAD file. Complex geometries with medium surface finishing and generally porous are quickly printed.
The Liquid Deposition Modeling (LDM) technology can be applied for the 3D-printing of advanced, traditional and composite ceramics.